xFlow (NetFlow and sFlow) Sensor Types
Some routers and switches can capture and export bandwidth usage data using the NetFlow and sFlow protocols. Both options are specially suited for bandwidth monitoring in high traffic networks.
Both technologies are quite similar and are commonly referred as "xFlows" in PRTG.
- NetFlow is a network protocol developed by Cisco Systems for collecting IP traffic information. Many of the larger Cisco IOS-enabled routers and switches support this feature. Besides Cisco devices also some routers from other vendors support NetFlow export (e.g. Juniper jFlow can export NetFlow data).
- sFlow is a cross-vendor standard and alternative to Netflow
xFlow sensors support Toplists (Top Talkers, Top Connections etc.), see Toplists.
How xFlow Monitoring works
You can measure bandwidth usage "by IP address" or "by application" in a network by using one of the xFlow protocols. They are the best choice especially for networks with high traffic (connections with 100s of megabit or gigabits). For xFlow monitoring the router gathers bandwidth usage data ("flows"), aggregates them and sends information about these flows to PRTG using UDP packets. When sampling is used (mandatory for sFlow) only information about every n-th packet is sent to PRTG which reduces CPU load a lot. Because the switch already performs a pre-aggregation of traffic data, the flow of data to PRTG is much smaller than the monitored traffic. This makes NetFlow the ideal option for high traffic networks that need to differentiate the bandwidth usage by network protocol and/or IP addresses.
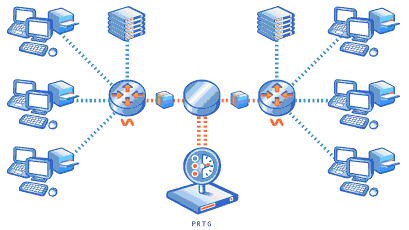
NetFlow Monitoring
PRTG supports flow monitoring using NetFlow with the following sensors types:
- NetFlow 5: Monitors switches using NetFlow V5.
- NetFlow 9: Monitors switches using NetFlow V9.
- NetFlow 5 (Custom): User configurable version of the NetFlow sensor.
- NetFlow 9 (Custom): User configurable version of the NetFlow sensor.
Before you can create NetFlow sensors, you must configure the NetFlow export on your switch/router. Configure the switch to send the NetFlow packets to the computer running a PRTG probe (either the local probe or a remote probe). The NetFlow port (port number that the UDP packets are sent to) and the flow timeout must be set to the same value in the router and in PRTG. Finally don't forget to open the NetFlow port in the PRTG system's firewall. Paessler supplies two test tools for debugging NetFlow installations as well as tips for the router setup (see below).
sFlow Monitoring
PRTG supports flow monitoring using sFlow with the following sensors types:
- sFlow: Monitors switches using sFlow.
- sFlow (custom): User configurable version of the sFlow sensor.
Before you can create sFlow sensors, you must configure the sFlow export on your switch/router. Configure the switch to send the sFlow packets to the computer running a PRTG probe (either the local probe or a remote probe). The sFlow port (port number that the UDP packets are sent to) must be set to the same value in the router and in PRTG. Finally don't forget to open the sFlow port in the PRTG system's firewall.
Limitations
On a powerful 2008 PC (Dual Core, 2.5 Ghz), you can process about 100,000 flows per second for one xFlow stream. Using sampling the number of actual flows can be much higher. When using complex filters, the value can be much lower. For example, with a router sending about 2,000 flows/second (which corresponds to mixed traffic at gigabit/sec level without sampling) you can expect to configure up to 50 NetFlow sensors operating properly. PRTG internally monitors its own NetFlow processing and you will see a decreased probe health reading as soon as NetFlow packets are not processed due to an overload.
If you experience an overload please consider using sampling or setting up multiple probes and distribute the NetFlow streams to them. We do not recommend adding more than 400 NetFlow sensors per PRTG probe.
Tools
Paessler NetFlow Generator: NetFlow Generator creates artificial NetFlow Version 5 data streams without the need for NetFlow compatible hardware. It is a perfect tool to test the NetFlow functionality of PRTG or other NetFlow compatible programs.
http://www.paessler.com/tools/netflowgenerator
Paessler NetFlow Tester: NetFlow Tester simply dumps the data of all NetFlow 5 packets that a computer receives from a Cisco router - useful when debugging bandwidth monitoring configurations based on NetFlow protocol.
http://www.paessler.com/tools/netflowtester
See also
- Comparison of Bandwidth Monitoring Sensor Types
- Toplists
- Paessler Knowledge Base: Configuration Tips for Cisco Routers and PRTG
http://www.paessler.com/support/kb/questions/20/ - Cisco Netflow information: http://www.cisco.com/go/netflow
- sFlow website: http://www.sflow.org
Keywords: Sensor,NetFlow